Constitutional Convention (Delaware)
Constitution (1787)
[Article I, Section 8]
Federal government has the following rights:
1) to lay and collect taxes, duties, imposts and excises
2) to pay the debts and provide for the common defense (Militia: continental army, navy - but less than two years to keep them) and general welfare of the United States
3) declare War
4) To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers
Constitution (1787)
[Article I, Section 8]
Federal government has the following rights:
1) to lay and collect taxes, duties, imposts and excises
2) to pay the debts and provide for the common defense (Militia: continental army, navy - but less than two years to keep them) and general welfare of the United States
3) declare War
4) To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers
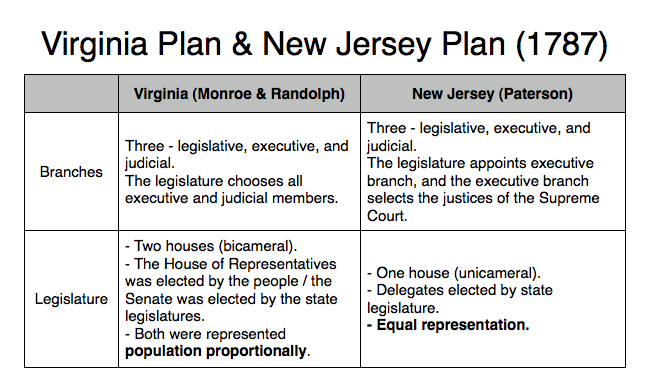
Connecticut Compromise (1787)
a.k.a. Great Compromise
- Branch : three.
- Legislature : bicameral;
- House of Representatives = population-weighted / elected by people
- Senate = equal representation / elected by state legislature
- 3/5 compromise : slaves = 3/5 human
- people -> legislative (congress) -> executive -> judiciary
side notes : For encouraging future settlement, South would not end slave trades for the next 20 years
a.k.a. Great Compromise
- Branch : three.
- Legislature : bicameral;
- House of Representatives = population-weighted / elected by people
- Senate = equal representation / elected by state legislature
- 3/5 compromise : slaves = 3/5 human
- people -> legislative (congress) -> executive -> judiciary
side notes : For encouraging future settlement, South would not end slave trades for the next 20 years
Northwest Ordinance (1787)
- Northwest Territory will be divided into 3~5 territories
- prohibited slavery, freedom of religion, rights to trials by jury
- once it reaches enough population (5000 white men), can apply for statehood
- Northwest Territory will be divided into 3~5 territories
- prohibited slavery, freedom of religion, rights to trials by jury
- once it reaches enough population (5000 white men), can apply for statehood
Bill of Rights (1789)
- Drafted mainly by James Madison
- Freedom of speech, press, religion, etc.
- Many Federalists (Hamilton) did not see the point of restating pre-assumed perambulatory clauses into another set of amendments, but anti-federalists (Republicans) claimed without proper written document these rights may be abused.
- Thomas Jefferson (out in France negotiating...wasn’t present in Constitutional Convention)
- Drafted mainly by James Madison
- Freedom of speech, press, religion, etc.
- Many Federalists (Hamilton) did not see the point of restating pre-assumed perambulatory clauses into another set of amendments, but anti-federalists (Republicans) claimed without proper written document these rights may be abused.
- Thomas Jefferson (out in France negotiating...wasn’t present in Constitutional Convention)
Judiciary Act of 1789
- Federalists made it (strong fed. gov.)
- Supreme court with 6 members + State courts
- court’s power to compel executive officials to do something
- power to make final decision in cases involving constitutionality of state laws (a.k.a. can rule over state laws)
- Federalists made it (strong fed. gov.)
- Supreme court with 6 members + State courts
- court’s power to compel executive officials to do something
- power to make final decision in cases involving constitutionality of state laws (a.k.a. can rule over state laws)